This course is intended for beginning, intermediate, and advanced levels.
After completing this section the student should be able to do the following:
- Define Visual Field
- Define Isopter
- List 2 methods of visual field testing
- Identify relative and absolute visual field defects
- Define target size and target brightness
- Define Scotoma
- State in degrees where isopters should generally fall on a kinetic visual field
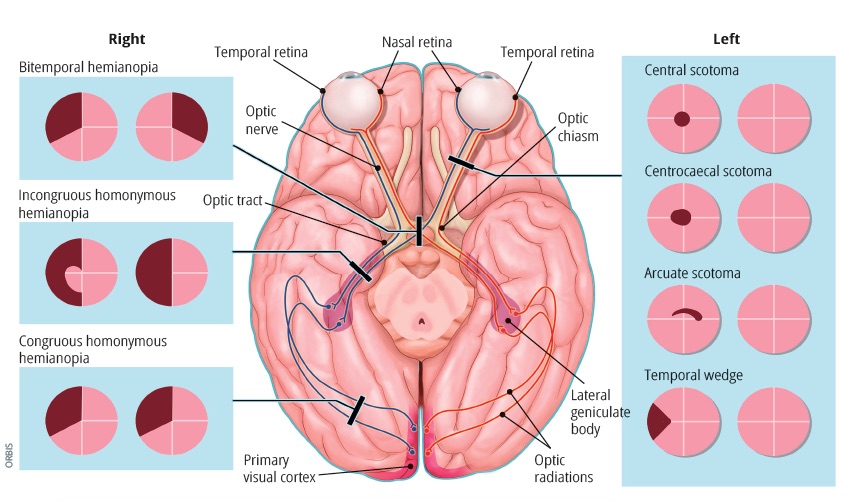
- Describe which side of the brain the impulse will end up on if an object is to the left side of the patient
- Describe which side of the brain the impulse will end up on if an object is to the right side of the patient
- Describe how the nasal and temporal fibers travel back the visual pathway
- List the 4 territories in the visual pathway
- Identify diseases that may cause territory I and territory II visual field defects
- Identify types of defects found in territory I problems
- Identify types of defects found in territory II problems
- Describe the makeup of the nerve fiber layer and how that results in certain visual field defects
- List the 3 parts of the nerve fiber layer and describe their anatomy
- Identify types of defects found in territory III problems
- Identify types of defects found in territory IV problems
- Identify what type of tumor could cause a bitemporal hemianopia
- Define bitemporal hemianopia
- Define right and left homonymous hemianopia
This course should take approximately 2 hours to complete.
This course has been approved by the AOA Commission on Paraoptometric Certification (CPC) for continuing education credit for use toward paraoptometric certification renewal.